The term "Open Banking" describes the practice whereby financial markets make their data available to other parties’ subject to government oversight. As scary as that seems, it's quite safe. In essence, banks are laying the groundwork for individuals to share their information with other parties on an opt-in basis.
This final point is essential to understand. Open banking is not a ruse to enable financial institutions to profit more readily from selling their client's personal information. On the contrary, open banking was established to enhance the banking institutions available to clients.
This is the rationale behind the concept. And by allowing access to data that they have traditionally kept private, they make it possible for new businesses and products to enter the market and use this information in beneficial and inventive ways.
How Open Banking Works?
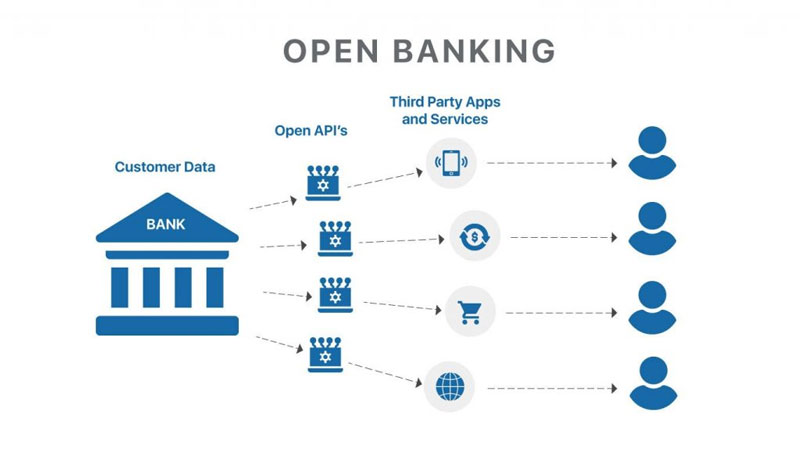
With financial inclusion, third-party payment systems and other monetary telecommunications companies can access consumer banking data. Customers must first provide permission to share their information, often through a terms & conditions contract and a corresponding online signed agreement. APIs are made available to third-party companies so that they may acquire the necessary shared data.
These APIs make it possible for customers to move money across accounts at different banks without having to go through the cumbersome processes that have traditionally been necessary. APIs may also parse an individual's purchase history to find ways to improve the shopping experience. A newly issued credit card with a lower APR or higher cash-back rewards would qualify, as would a checking account that delivers a higher rate of return.
Mechanism of Open Banking
Data is at the center of any open banking API request. It helps render quick and easy data accessibility the top priority for any cutting-edge solution. The reality for most fintech companies is more akin to a data swamp than a data lake, with fragmented sources of data, an assortment of legacy and cutting-edge data types, and a tangled web of administrative roadblocks. An effective integration system is needed for this endeavor.
Application integration and data virtualization are the two most common approaches to open banking. When your APIs are physically integrated, they can make safe, direct calls to your backend services.
Advantages of Open Banking

Connecting data (through APIs) from many accounts enables efficient sharing between banks, customers, and 3rd-party payment service suppliers. This is partly due to interruptions from 3rd-party suppliers, which have been gradually altering the banking business's user experience and business conditions.
Clients and businesses alike benefit from the convenience of online access to their linked accounts. The more information a lender has about a customer's financial status, the better they can evaluate the risk and develop practical arrangement terms. It also aids the customer in learning more about their financial status to make more informed choices.
- Customers who have grown up with digital technologies and are now joining the workforce have come to demand real-time customer care from their financial services providers.
- Companies might reduce their operating expenses by using the modern and developed technology.
- Possibility of a new sales channel with a broader product selection.
- Reduced time needed to bring new items to market.
Influence of Open Banking On The Economy
By providing access to previously unavailable financing options, open banking helps small enterprises outperform industry giants. This has opened the door for new enterprises to enter the marketplace with lower, more cost-effective options for conventional financial products.
There will be new entrants to the banking sector, and the larger, more established institutions will be required to work hard to keep their position. The goal is to decrease expenditures while simultaneously promoting cutting-edge technologies and enhanced quality of service to customers. Using fintech, financial organizations may focus on building connections with their consumers rather than merely processing transactions.
Risks of Open Banking
Customers and banking institutions have placed a high premium on maintaining the privacy and security of their financial information and other personally identifiable information. On the other hand, just as with any other digitally oriented service.
Most issues with APIs derive from inadequate security, phishing, and malicious insiders. APIs do not come without a particular element of danger, though. A further problem is the availability of malware that third-party app developers developed. This virus can infect a user's account and delete all their data. Also, there is the possibility that payment service companies would improperly handle the information of their clients to acquire a competitive edge.
The application programming interface (API) security technology available nowadays is exceptionally advanced and is a perfect match for the requirements of open banking. In order to control API access and flow, it possesses robust authorization and security features. The following are some of the essential capabilities:
- Monitoring all ongoing traffic via gateways, particularly integrated micro gateways by a single centralized system
- You have the ability to create access and security restrictions between distinct customers, such as rate limitation and filtering.
Is Open Banking safe?
Yes, open banking is entirely safe. Open banking service providers have access to consumer information using APIs. It is a tried and tested technology primarily used in the larger digitalization. They are intended to establish a safe link between third-party payment processors and their clients' accounts.
Open banking eliminates customers' need to provide passwords, in contrast to traditional banking practices such as screen scraping. They just authenticate themselves using a secure application programming interface connection to their respective banks to allow their account access.
Open banking ensures:
- Control of the data: Open banking technologies allow specific access restrictions for both the user and the data proprietors, per the standards and data protection standards.
- Access to and transfer data without risk: Open accounting and application programming interfaces (APIs) are a tried and tested technology.
- Data reduction is achieved through open banking, which places the customer in charge of their data. Users are given the option to disclose as much or as little personal data as they wish.



